Matplotlib Beschriftungen und Titel
Erstellen Sie Beschriftungen für einen Plot
Mit Pyplot können Sie die Funktionen xlabel() und ylabel() verwenden, um eine Beschriftung festzulegen für die x- und y-Achse.
Beispiel
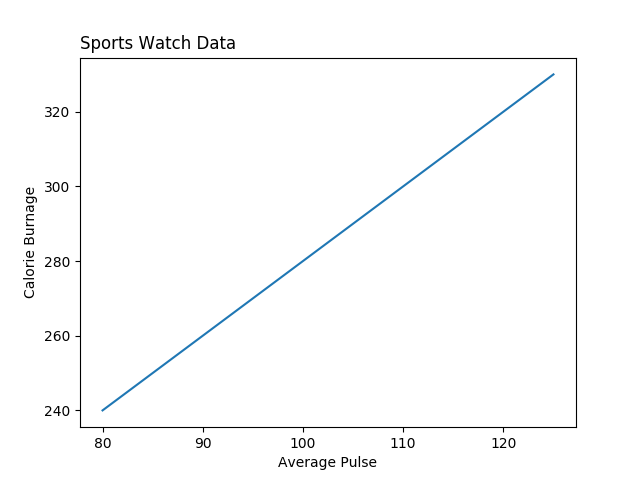
Fügen Sie Beschriftungen zur x- und y-Achse hinzu:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([80, 85, 90, 95, 100, 105, 110, 115, 120, 125])
y = np.array([240, 250, 260, 270, 280, 290, 300, 310, 320, 330])
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel("Average Pulse")
plt.ylabel("Calorie Burnage")
plt.show()
Ergebnis:
Erstellen Sie einen Titel für eine Handlung
Mit Pyplot können Sie die Funktion title() verwenden, um einen Titel für die Handlung festzulegen.
Beispiel
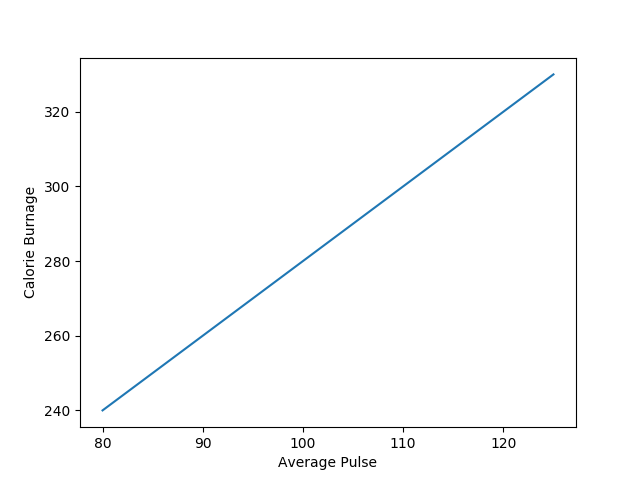
Fügen Sie einen Plottitel und Beschriftungen für die x- und y-Achse hinzu:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([80, 85, 90, 95, 100, 105, 110, 115, 120, 125])
y = np.array([240, 250, 260, 270, 280, 290, 300, 310, 320, 330])
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.title("Sports Watch Data")
plt.xlabel("Average Pulse")
plt.ylabel("Calorie Burnage")
plt.show()
Ergebnis:
Legen Sie Schriftarteigenschaften für Titel und Beschriftungen fest
Sie können den Parameter fontdict verwenden xlabel(), ylabel(), und title() um Schriftarteigenschaften für den Titel und die Beschriftungen festzulegen.
Beispiel
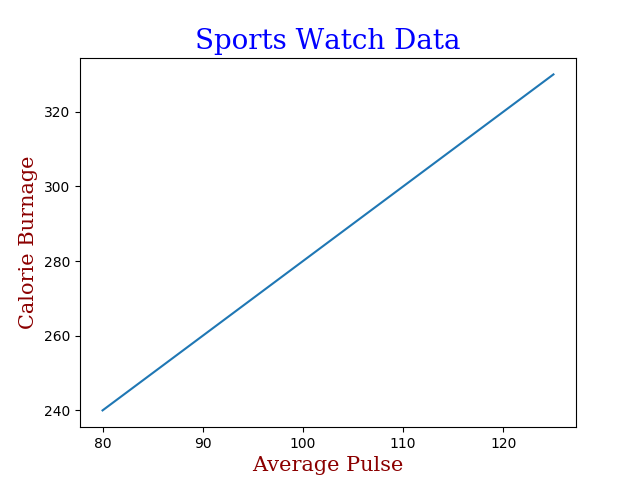
Legen Sie Schriftarteigenschaften für Titel und Beschriftungen fest:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([80, 85, 90, 95, 100, 105, 110, 115, 120, 125])
y = np.array([240, 250, 260, 270, 280, 290, 300, 310, 320, 330])
font1 = {'family':'serif','color':'blue','size':20}
font2 = {'family':'serif','color':'darkred','size':15}
plt.title("Sports Watch Data", fontdict = font1)
plt.xlabel("Average Pulse", fontdict = font2)
plt.ylabel("Calorie Burnage", fontdict = font2)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()
Ergebnis:
Positionieren Sie den Titel
Sie können den Parameter loc in title() verwenden, um den Titel zu positionieren.
Gesetzliche Werte sind: 'left', 'right', und 'center'. Der Standardwert ist 'center'.
Beispiel
Positionieren Sie den Titel links:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([80, 85, 90, 95, 100, 105, 110, 115, 120, 125])
y = np.array([240, 250, 260, 270, 280, 290, 300, 310, 320, 330])
plt.title("Sports Watch Data", loc = 'left')
plt.xlabel("Average Pulse")
plt.ylabel("Calorie Burnage")
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()
Ergebnis: